Treatment Options for Granular Corneal Dystrophy
In many scenarios, additional treatments may be recommended alongside the use of scleral lenses.
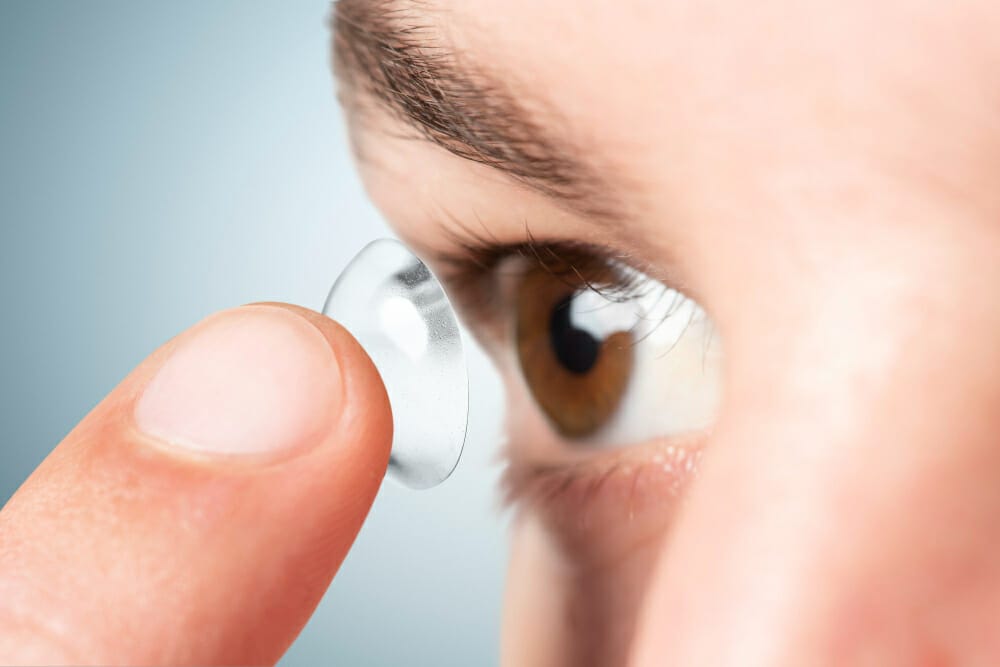
For non severe recurrent corneal erosions (RCEs) associated with granular corneal dystrophy, bandage soft contact lenses coupled with antibiotic drops or antibiotic ointment may be utilized.
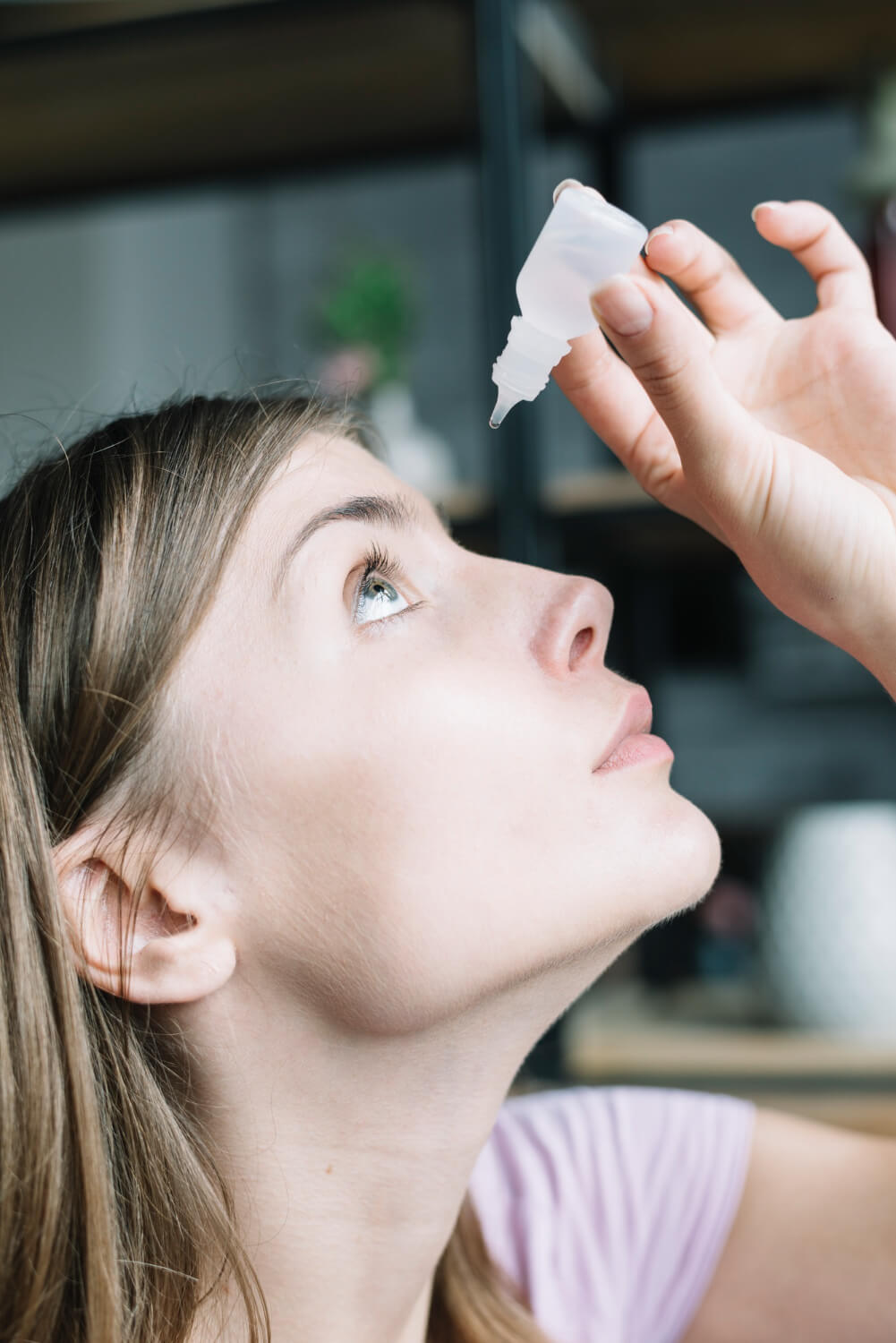
Further prevention of RCEs can potentially be achieved by implementing a regimen of sodium chloride drops or artificial tear lubricating drops during the day, accompanied by the application of lubricating ointment during the night.
In instances where RCEs continue despite these preventative measures, surgical interventions may come into play. Procedures such as corneal punctures, involving needle punctures to facilitate the adhesion of eye tissue to corneal cells, could be suggested. Another option is Phototherapeutic Keratectomy (PTK), a laser treatment aimed at eradicating corneal deposits and promoting the binding of eye tissue to the top layer of corneal cells.