Treatment Options for Accommodative Insufficiency
Fortunately, there are treatment options available for accommodative insufficiency that can help improve vision and alleviate symptoms.
Eyeglasses & Contact lenses
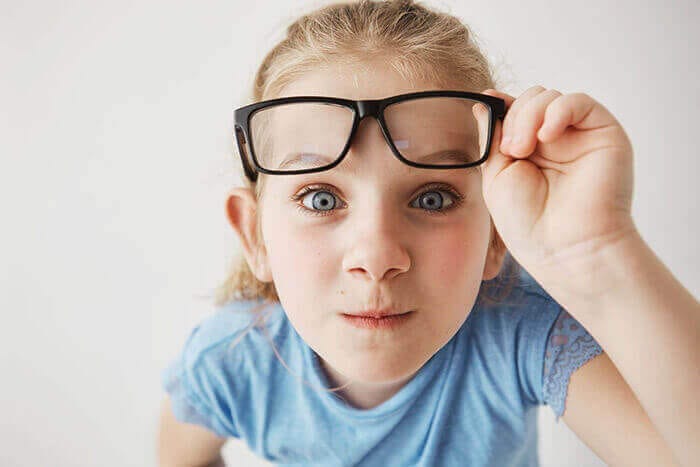
One of the most common and effective treatments for accommodative insufficiency is eyeglasses. Prescription glasses can help correct refractive errors and improve the eye's ability to focus on near objects. Depending on the severity of the condition, glasses with single or progressive lenses may be recommended. Single lenses correct either near or far-sightedness, while progressive lenses gradually change the prescription from the top to the bottom of the lens, allowing for clear vision at all distances.
Contact lenses can also be an effective treatment option for accommodative insufficiency. Depending on the patient's individual needs, either soft or rigid gas permeable contact lenses may be recommended. Contact lenses can help correct refractive errors and improve the eye's ability to focus on near objects.
Vision therapy
Vision therapy is a non-invasive, non-surgical treatment option that can be effective for treating accommodative insufficiency. This type of therapy involves a series of exercises and activities designed to improve visual skills, including accommodation, tracking, and binocular vision. Vision therapy is typically conducted by our vision therapist under the guidance of our trained optometrist and can take several months to complete.
Prism lenses
Prism lenses are another treatment option for accommodative insufficiency. These lenses are designed to help align the eyes and improve binocular vision, which can reduce symptoms such as double vision and eye strain. Prism lenses can be added to eyeglasses or contact lenses and are often used in conjunction with vision therapy.
Atropine eye drops
Atropine eye drops are a medication that can be used to treat accommodative insufficiency. These drops work by dilating the pupil and relaxing the muscles that control accommodation, which can improve the eye's ability to focus on near objects. Atropine eye drops are typically used as a short-term treatment and are not recommended for long-term use.
Surgery
In rare cases, surgery may be recommended to treat accommodative insufficiency. This typically involves either altering the shape of the cornea or inserting an intraocular lens implant to correct refractive errors. Surgery is typically only recommended in severe cases that do not respond to other treatment options.
It is important to note that the best treatment option for accommodative insufficiency will depend on your needs and the severity of your condition. Additionally, practicing good eye habits such as taking frequent breaks when doing near work, maintaining proper lighting, and wearing appropriate eyewear can also help alleviate symptoms and improve visual function.