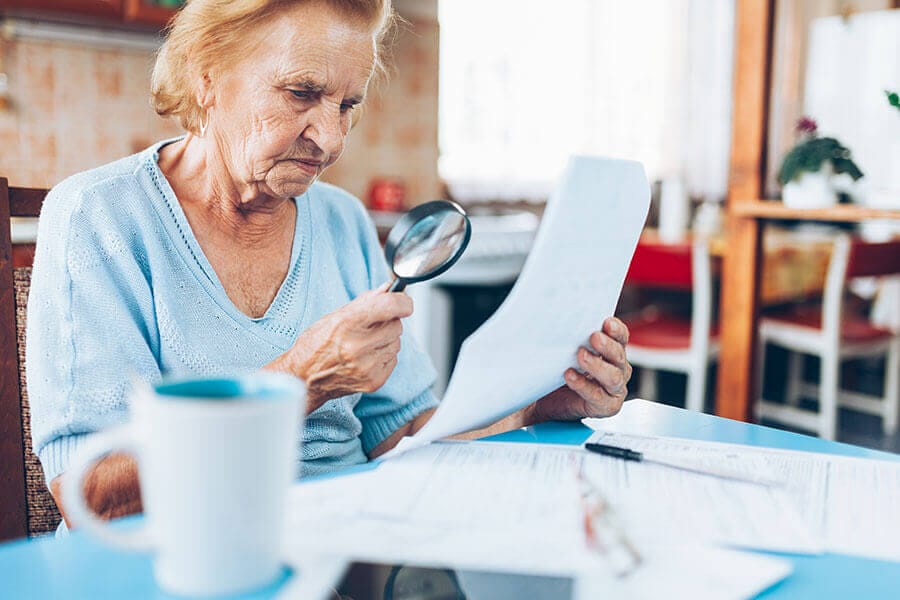
Are You Struggling to See Objects Up Close? Learn More About Hyperopia (Farsightedness) Symptoms
Here are some of the most common symptoms of hyperopia:
Blurry vision
Patients with hyperopia often experience blurry vision when looking at objects up close. This can make it difficult to read, write, or perform other tasks that require close-up vision.
Eye strain
People with hyperopia may also experience eye strain or fatigue when performing tasks that require near vision. This can be particularly noticeable when reading, writing, or using a computer for extended periods of time.
Headaches
Hyperopia can also cause headaches, particularly after performing tasks that require close-up vision. This can be due to the increased strain on the eye muscles as they try to focus light properly.
Squinting
Patients with hyperopia may find themselves squinting in an effort to see objects more clearly. Squinting can help to temporarily improve vision by narrowing the amount of light entering the eye and improving focus.
Difficulty with night vision
Hyperopia can also cause difficulty with night vision, particularly when driving. This is because the eye may struggle to adjust to changes in light levels, making it difficult to see clearly in low-light conditions.
Struggling to see objects at a distance
While hyperopia is typically associated with difficulty seeing objects up close, it can also cause problems with distance vision. Patients may find it difficult to see objects in the distance, such as road signs or television screens.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, or if you are concerned about your vision in general, we encourage you to schedule an appointment at our optometry clinic. A comprehensive eye exam can help to diagnose hyperopia and other vision problems, and we can provide you with personalized recommendations for treatment, including glasses, contact lenses, or vision therapy.